GIS & BI
What is a GIS?
A geographic information system (GIS) is a tool for collecting, storing, analysing and visualising geographic data. It allows data to be represented in the form of interactive maps, making it easier to understand and take decisions.
The value of GIS is that it allows geographic data to be manipulated more efficiently and accurately than a traditional map. Data can be analysed in a variety of ways, which can help decision-makers understand spatial relationships and trends in geographic data. GIS can be used in many fields, such as urban planning, environment, transport planning, natural resource management, urban design, security and many others.
The difference between a GIS and a map?
A map is a visual representation of geographic information, while a GIS is a computer system that collects, stores and analyses this information. In other words, a map is an end product that can be created from the data stored in a GIS. A map can be used to visualise geographical information, but it does not allow for the same flexibility and analysis possibilities than GIS.
We are at your disposal to help you find the best solutions for your needs!
Information technology
IT experts at your service
We intervene throughout the entire software life cycle to carry out all or part of your projects and, if necessary, act as a co-worker or specialised subcontractor.
Our organisational capacity is flexible and wide-ranging. Our projects range from a few days to several months or years. Teams range from 1 to 10+ people on a shared or full-time basis on your project.
We practice agile (Scrum, Prince2 Agile) or classical (Waterfall, V-cycle) project management methods. We are also HERMES 5 certified for project and program management.
What can we do for you?
Audit and automations
Techno redesign and revitalisation
Development
For which topics and activities?
Information System
- Development of data-centric systems
- Optimisation or redesign of operating procedures
- Ergonomic UX / UI work
- Computerisation of work processes
- Multi-platform web systems
- Agile process and support
- Adaptive project management methods (Hermes, Scrum, Prince2…)
- TMA
Geographical Information System
- Deployment of proprietary and open-source GIS systems
- Development of integrated tools
- Encapsulation of GIS components in web and mobile applications
- Interactions between GIS and enterprise IS
Orchestrated system
- Orchestration of business processes (automation, ETL chains)
- Micro-services and scalable architecture
- Multi-tier development, BackOffice / Frontoffice
- Operational support and monitoring
Scientific computing

- Deployment of proprietary and open-source GIS systems
- Development of integrated tools
- Encapsulation of GIS components in web and mobile applications
- Interactions between GIS and enterprise IS
Infrastructure and architecture
- Software architecture definition
- Hosting solution (data centres in Switzerland)
- Deployment and Support
- Maintenance and Monitoring
Computer Vision & Artificial Intelligence
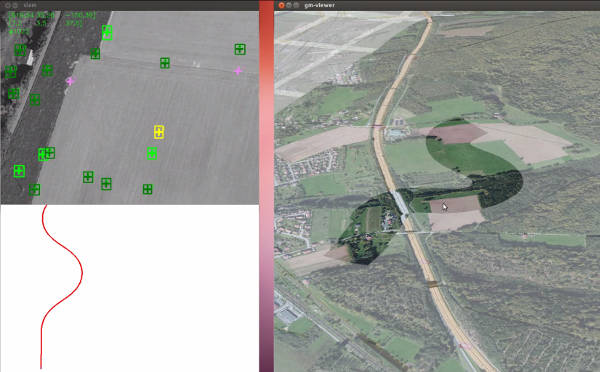
Using geo-referenced aerial video
Our findings
Drone systems or other means of taking video from the air should focus on the operational purpose and use.
In most contexts, video alone is not sufficient. Its use in a geographical context is essential.
Our solution
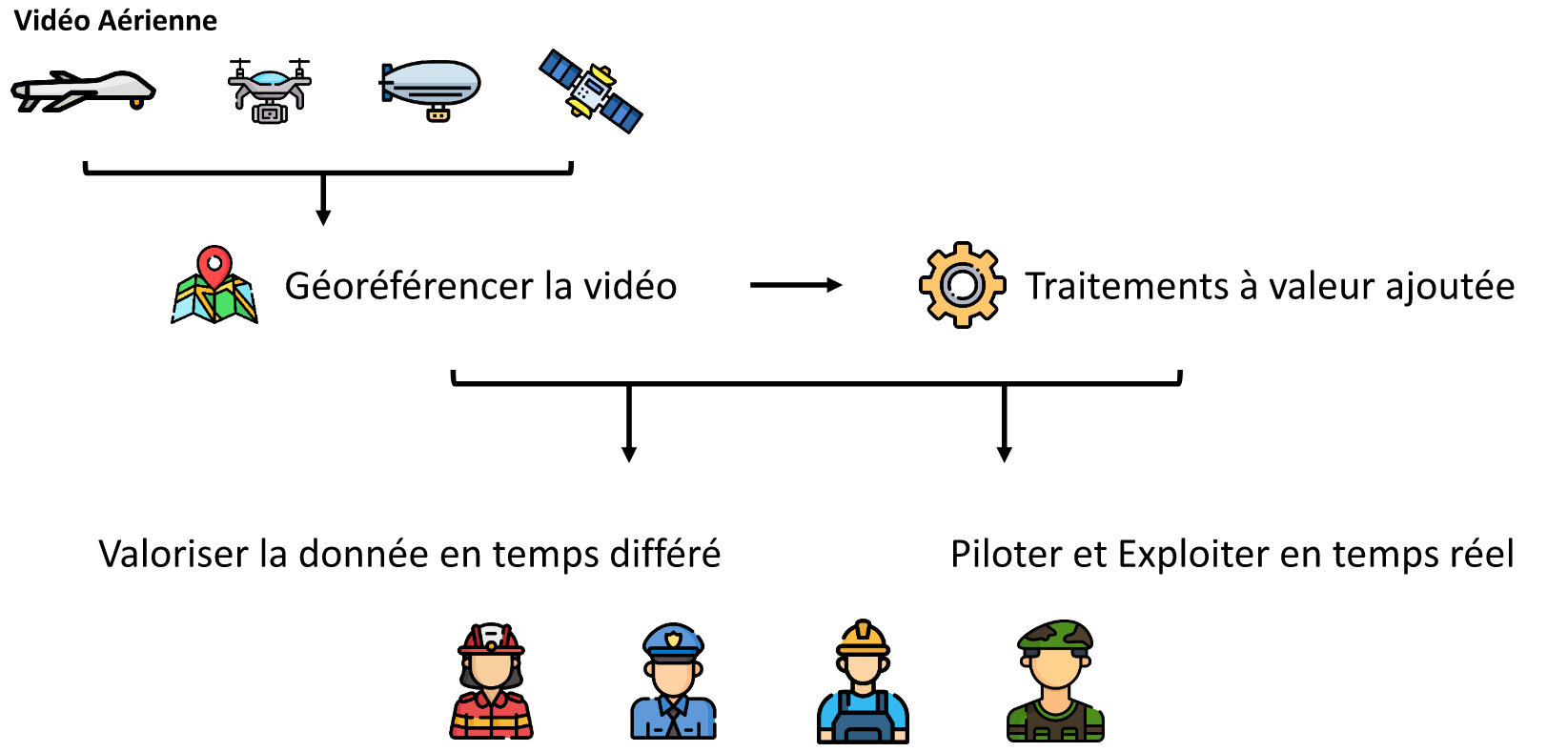
- Use sensor information to locate the video.
- Integrate value-added processing to project, contextualise and augment the video.
- Retrieve metadata, georeference and integrate processing without interrupting the video stream and with minimal latency.
Your video sensors are insufficient to provide the necessary metadata? We advise and provide them if needed!
Some examples of achievements
Geo-augmented video
These developments make it possible to integrate geographical data into the video stream for viewing on the ground or directly in flight.
Objectives:
- Displaying geographical markers to help analyse the videos
- Sharing geo-referenced objectives between tactical situation keeping and video analysis
- Automatically hide geo-defined regions
- etc.
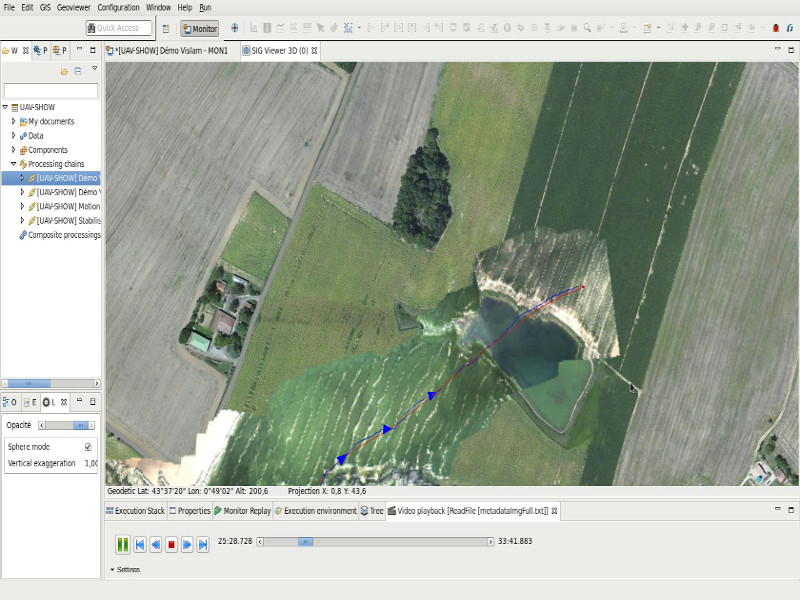
Real-time orthoimages
These developments make it possible to produce orthoimages in real time during the flight and to visualise them right up to the operational stations on the ground.
Objectives:
- Bringing fresh images into the map view as quickly as possible
- Quickly take the measure of a crisis situation (flooding, fire, etc.)
- etc.
Multiple tracking
These developments allow vehicles to be detected and tracked from fixed or mobile cameras.
Objectives:
- Detecting and tracking vehicles
- Measuring speeds
- Detecting intrusions in a defined area
- etc.
Object tracking
These developments allow objects to be detected and tracked in real time or in post-processing.
Objectives:
Hanging a target or visual cue
- Driving optronics to keep a target in the field
- Flying a drone to track a target autonomously
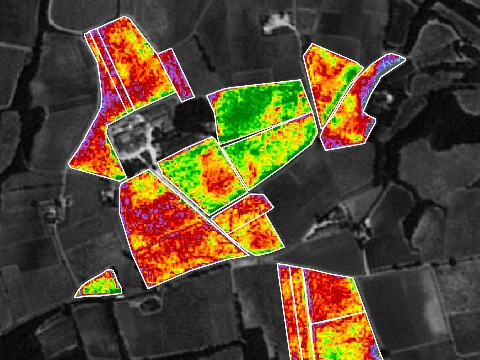
Recognition and data collection
lidar + lampadaire
roadmapper
corps et floutage
Sky & Space
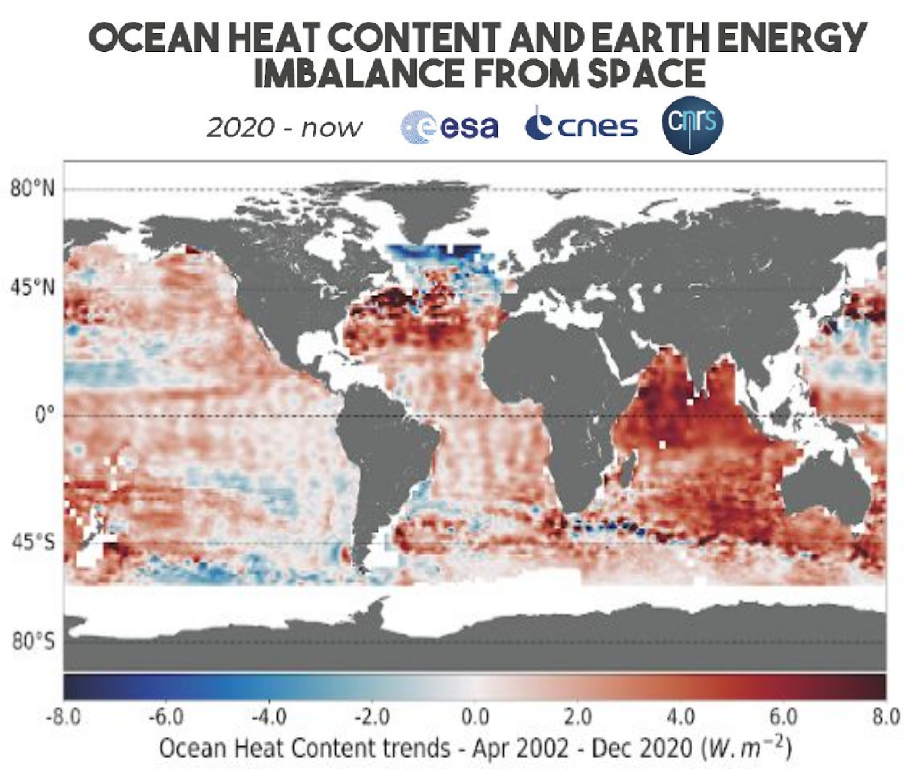
Earth observation services
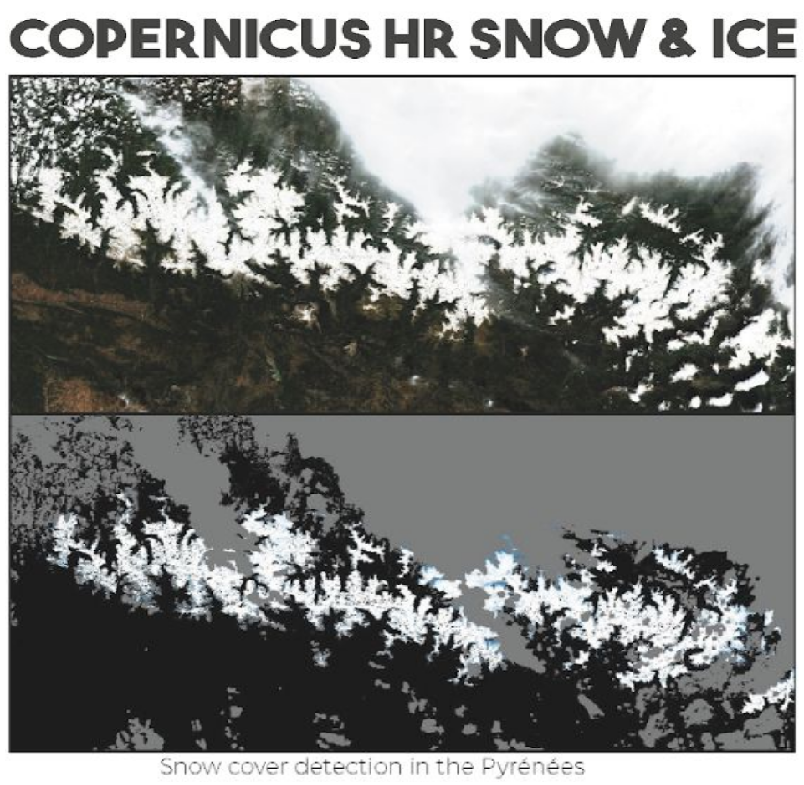
The emergence of user services for earth observation is one of our major development axes within the framework of Copernic (ex-GMES) and within the broader framework of “integrated applications”. These observation services allow the creation of imagery and analysis based on geospatial data.
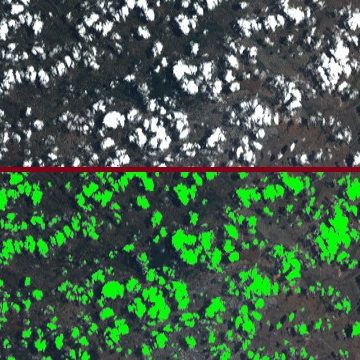
We have recognised expertise in geometric modelling of sensors, which is essential for image projection and ortho-rectified image generation. Our experience in image processing ranges from SAR imaging to high-resolution optical imaging. We offer powerful technical solutions: shape recognition, cloud detection, radiative transfer modelling, image compression, image co-location…
Climate change studies, snow and ice, hydrological modelling, inland water quality, segmentation and classification by deeplearning, cloud detection, fluorescence observation … the fields of application are countless!